Introduction
In the world of healthcare, reliable nutrition is critical for individual healing. One significant approach employed to guarantee appropriate dietary intake is enteral feeding. This post delves deep right into "The Function of Enteral Feeding in Patient Recovery: A Course Overview," exploring its importance, methodologies, and the training offered to healthcare professionals involved in this process.

Enteral feeding describes the delivery of nutrients directly right into the intestinal tract with a tube. It is frequently used when patients can not take in food orally due to different clinical conditions, such as neurological conditions, cancers, or serious injuries. Understanding enteral feeding's role in client recovery is essential for doctor, including registered nurses and assistance workers that involve with clients needing this type of nutrition.
This thorough overview will also discuss relevant training courses available for experts seeking to enhance their abilities in enteral feeding practices. With search phrases like "ndis peg feeding training," "enteral feeding support course," and "peg training for nurses" peppered throughout, we aim to offer a comprehensive understanding of the area while making certain availability for all readers.
The Role of Enteral Feeding in Patient Recuperation: A Training Course Overview
What is Enteral Feeding?
Enteral feeding involves providing nutrients directly into the gastrointestinal system via a tube when dental consumption is insufficient or impossible. This technique can be life-saving for clients struggling with problems that hinder swallowing or digestion.
- Types of Enteral Feeding: Nasogastric (NG) Tube: Placed with the nose right into the stomach. Orogastric Tube: Placed through the mouth right into the stomach. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) Tube: Operatively positioned within the belly via the stomach wall.
The choice of tube commonly depends upon the period of feeding required and individual patient needs.
Why Is Enteral Nutrition Important?
Nutritional assistance through enteral feeding plays a crucial function in:
- Maintaining Nutritional Status: Prevents poor nutrition and helps preserve muscle mass mass. Improving Healing Times: Adequate nutrition can quicken recuperation from surgical procedures and illnesses. Enhancing Quality of Life: Correct nourishment affects general wellness and energy levels.
Indications for Enteral Feeding
Understanding when to initiate enteral feeding is important for ideal client care. Common indications consist of:
- Neurological problems (e.g., stroke) Cancers impacting swallowing Severe burns or stressful injuries Chronic diseases affecting appetite
Training and Courses Available
To properly administer enteral nourishment, health care experts require specialized training. Here are some essential courses:
Ndis PEG Feeding Training
This training course concentrates on making it possible for support workers to aid people with PEG tubes properly and compassionately.
Enteral Feeding Support Course
Designed for registered nurses and allied wellness professionals, this training course covers important strategies associated with carrying out and keeping track of enteral feeds.
PEG Training for Nurses
Specialized training that emphasizes scientific techniques surrounding PEG tube insertion, maintenance, and repairing complications.

PEG Training Courses
Various organizations offer courses that provide both theoretical understanding and sensible abilities connected to secure systems.
PEG Feeding Course
A detailed summary designed particularly for caretakers in charge of handling people on PEG feeds.
What Is PEG Feeding?
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) feeding refers specifically to supplying nutrients directly into the tummy using a tube placed by means of an endoscopic procedure. It's typically selected when long-term nutritional support is necessary.
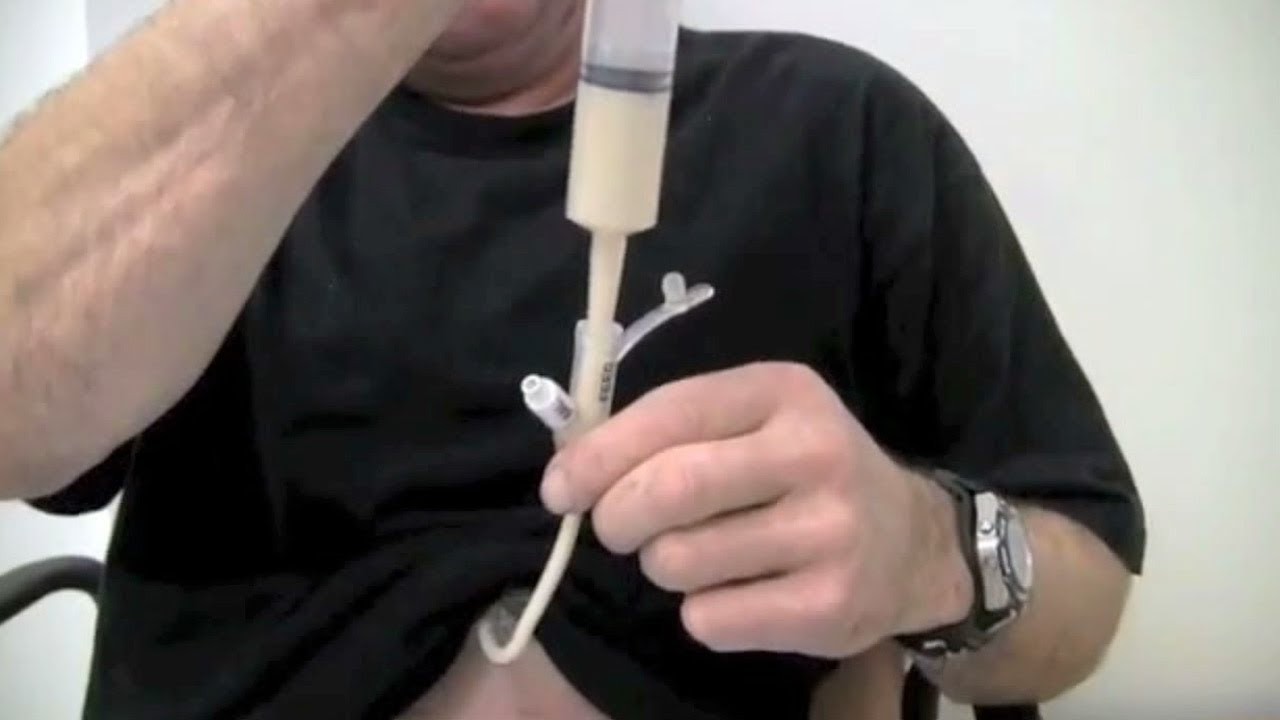
Components of Effective Enteral Nutrition
Nutritional Formulas Utilized in Enteral Feeding
Different solutions exist based on patient demands:
- Standard solutions: For those with typical digestion. Hydrolyzed solutions: For people with damaged digestion or absorption.
It's important to choose a formula that matches each individual's specific metabolic requirements.
Administration Methods
Enteral feeds can be provided using numerous techniques:
Bolus Feeding: Huge amounts supplied at once. Continuous Infusion: Slow management over 24 hours. Intermittent Feeding: Routine periods throughout daytime hours.Understanding these methods permits healthcare providers to customize strategies according to private patient requires effectively.
Monitoring Clients Obtaining Enteral Nutrition
Assessing Nutritional Requirements Regularly
Routine analyses assist make certain that each person receives sufficient nutrition tailored to their developing requirements.
Identifying Complications Early
Vigilant tracking can aid protect against prospective difficulties related to enteral feeding such as:
- Tube blockage Infection at insertion sites Gastrointestinal discomfort
Regular assessments facilitate timely interventions that boost results significantly.
Psychosocial Facets of Enteral Feeding
Addressing Person Problems about PEG Tubes
Patients may experience stress and anxiety concerning their new dietary routine or worries concerning their appearance due to noticeable tubes. Open communication can relieve fears while promoting adherence to treatment protocols.
Family Education and Support
Educating relative regarding enteral feeding enhances home treatment quality when individuals transition from healthcare facility environments back home.
Frequently Asked Inquiries (Frequently asked questions)
1. What are common indications for utilizing enteral feeding?
Common signs consist of neurological disorders impacting swallowing, cancer treatments leading to anorexia, serious head injuries, or any type of problem where oral intake isn't viable.
2. Exactly how does one know if a client requires PEG feeding?
Healthcare specialists assess swallowing abilities alongside nutritional requirements; if dental intake fails constantly over time, PEG could be indicated.
3. What types of formulas are made use of in enteral nutrition?
Formulas vary from basic blends suitable for many individuals to specialized hydrolyzed alternatives designed for those with unique digestion requirements.
4. Exist risks connected with enteral feeding?
Risks include infection at site insertion points, aspiration pneumonia from Get more information misplacement, or difficulties stemming from inaccurate formula management methods.
5. How often must nutritional assessments occur?
Regular assessments ought to happen regular initially; modifications might be made more regularly if significant adjustments emerge in health and wellness status or weight variations occur rapidly thereafter.
6. What training do healthcare specialists need for providing PEG feeds?
Training needs to incorporate makeup understanding regarding tube positioning & & administration procedures together with examining emotional impacts on individuals receiving this kind of nutrition treatment effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding "The Duty of Enteral Feeding in Patient Recovery" stays pivotal within medical care disciplines focused on supplying optimal dietary treatment tailored towards private person situations-- specifically those including facility conditions requiring alternate courses like PEG tubes efficiently handled by qualified specialists throughout several settings including nursing duties & & helpful solutions alike!
By fostering expertise through structured training courses such as ndis peg feeding training & & various other pertinent programs focused on improving caregiver competency levels allow much better outcomes inevitably benefiting both clients' physical well-being while enhancing their overall quality-of-life experiences considerably over time!
Investing time right into mastering these elaborate details encourages devoted specialists committed toward all natural methods rooted securely within evidence-based techniques throughout all stages involved-- thus making certain no individual left behind regardless where they stand along their recuperation trip ahead!